360 Protective Marking is an add-in for Microsoft Office and IBM Notes that enforces positive classification of documents/emails at the point of save, print and send. It is available for Outlook, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Visio and Notes email.

Classify, label and add metadata at the point of creation
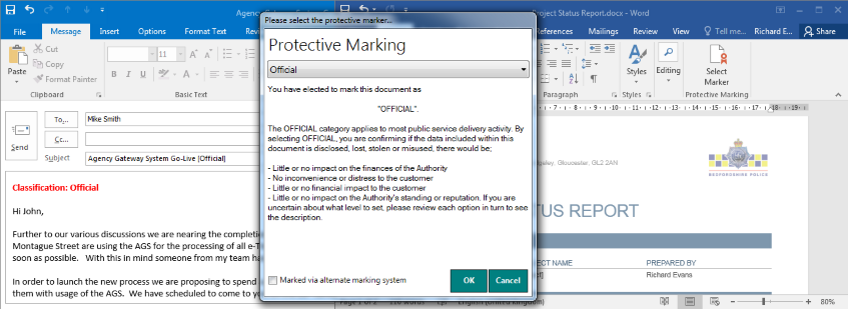
360 Protective Marking enables users to classify their documents and emails when they are writing them. When the user goes to save, print or send they are prompted to select a classification which applies metadata to the document or email. The classification options can be tailored to your organisation needs and can include retention periods alongside standard classification which can be used by a records and document management system.
Key features
- Positive selection of a marker
- Stores classification metadata with each document or email
- Office metadata available to SharePoint
- Mark Header, Footer or Subject with the visual description
- Custom markers and help descriptions
- Prevents email from when a classification is downgraded
- Enforce consistent labeling
- Enable mail gateways to enforce routing rules
- Development services available
Classifications for Microsoft Exchange, Outlook, Office, and IBM Notes
360 Protective Marking enables Public Sector organisations and suppliers to meet the UK Government Security Classifications requirements for the latest email and office software releases, including: General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ISO 27001 (the international information security standard), Government Security Classification Policy (GPMS), Government Protective Marking Scheme, etc.
360 Protective Marking is also available for older versions including Microsoft Exchange, Microsoft and Microsoft Office 2010, 2013 & 2016 and IBM Notes 9 and earlier versions of Lotus Notes.
Electronic Document and Records Management classification of content
360 Protective Marking can be configured to apply EDRM classifications to the metadata of content when it is created and edited. The information applied is often due to legal obligations or business need and defines:
- How active documents are used
- Which library do documents go to
- What kinds of documents should become records
- Categorise records which require similar treatment
- Who is the primary record owner
- How long they must be kept for
- What happens to them after retention period is up




